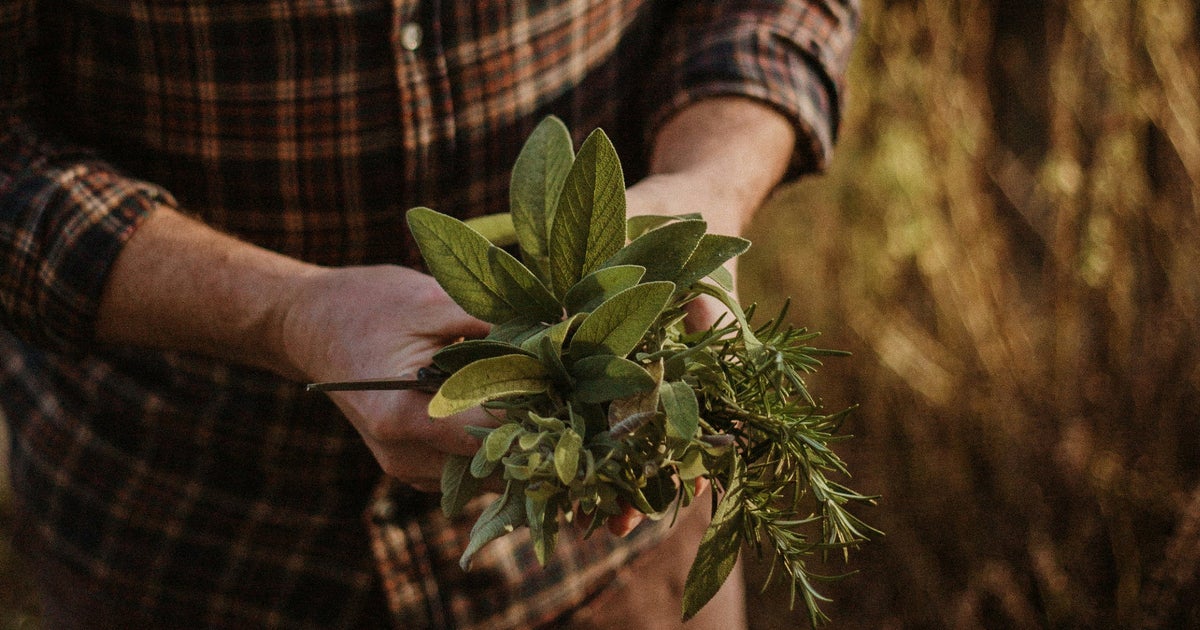
Recent research has highlighted the significant role that diet plays in brain health, revealing that while we cannot control all risk factors for dementia, certain foods may contribute positively to our cognitive well-being. According to the Alzheimer’s Society UK, a diet abundant in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and fish promotes long-term health and minimizes the risk of dementia.
Moreover, researchers have identified a “bi-directional relationship between the microbiome and anxiety,” suggesting that diets low in fiber and high in sugar can lead to poorer sleep quality. Notably, rosemary has emerged as a herb that may enhance blood circulation to the brain, potentially benefiting mental health in several ways.
A recent study published in the journal Antioxidants explored the effects of carnosic acid, a compound found in rosemary, linking it to improved outcomes for dementia in mouse models. The research reported that this compound aids in the elimination of proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Carnosic acid is renowned for its neuroprotective properties, as well as its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities. However, due to its inherent instability, researchers developed a synthetic alternative called diAcCA, which offers a more consistent and stable form suitable for testing.
In trials with mice exhibiting amyloid plaques characteristic of Alzheimer’s, diAcCA demonstrated a reduction in harmful proteins without any adverse side effects. The lead author of the study remarked, “We did multiple different tests of memory, and they were all improved with the drug. And it didn’t just slow down the decline; it improved virtually back to normal.”
Further probing into the benefits of rosemary has yielded interesting results. A double-blind, randomized trial conducted in 2024 indicated that rosemary could enhance both prospective and retrospective memory, mitigate anxiety and depression, and elevate sleep quality among university students.
Additionally, a 2020 investigation showed that Japanese men suffering from mood disturbances achieved significant improvements in mood and sleep after consuming rosemary extract over four weeks. Furthermore, rosemary tea consumption has been associated with lower levels of anxiety and depression biomarkers in healthy individuals.
An additional 2021 study linked the use of lavender and rosemary aromatherapy to enhanced cognitive function, reduced anxiety levels, and improved sleep patterns in older adults with diabetes.